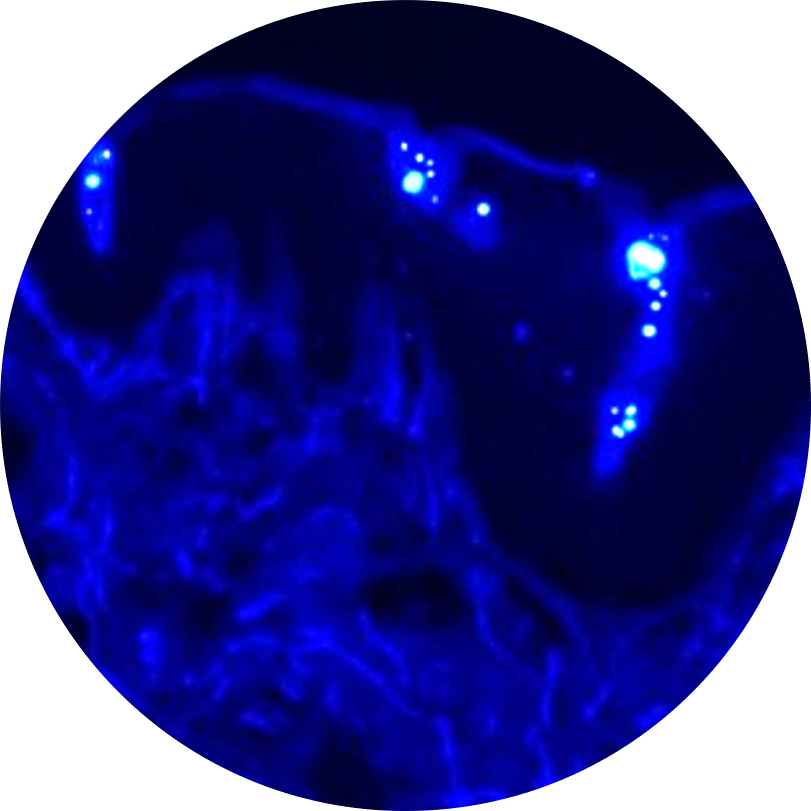
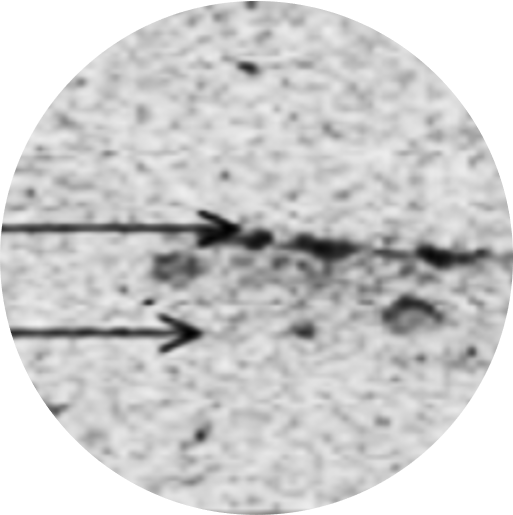
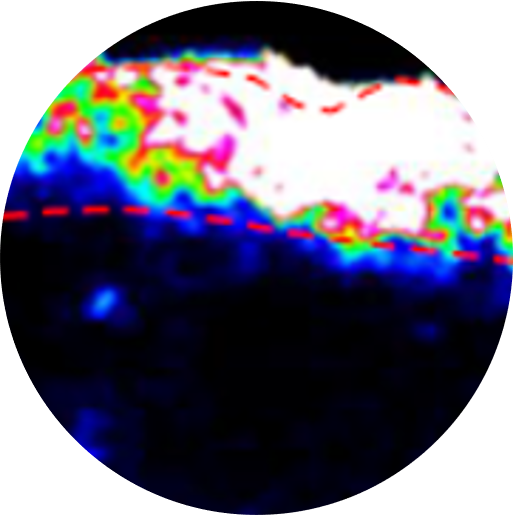
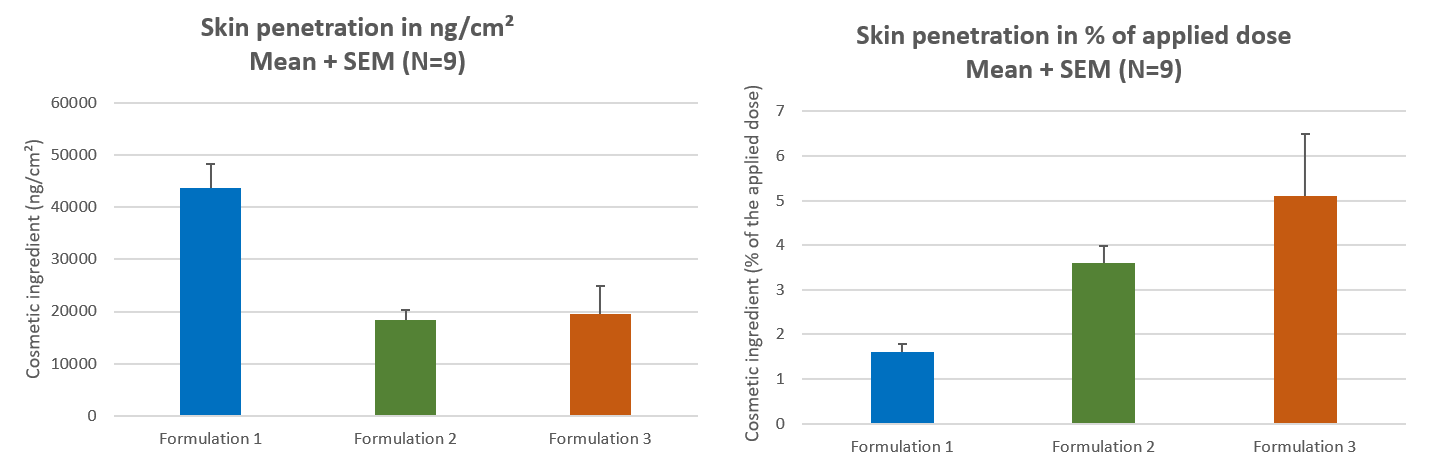
The purpose of the in vitro dermal absorption testing, also known as in vitro permeation testing (IVPT) or in vitro percutaneous absorption, is to provide a measurement of the absorption or penetration of a substance through the skin barrier and into the skin. Dermal penetration studies are conducted to determine how much of a chemical penetrates the skin, and thereby whether it has the potential to be absorbed into the systemic circulation.
Therefore, knowledge of dermal absorption phenomena is essential for:
- Safety issues: quantities absorbed can be taken into consideration in toxicological risk assessment to extrapolate human exposure and calculate the safety margin.
- Therapeutic aspects: quantities penetrated can be taken into consideration to predict the therapeutic concentration at the target sites in skin tissue.
Dermal absorption studies are conducted using in vitro methods in compliance with the OECD Test Guideline 428.
In vitro dermal absorption studies are applied in different sectors and for different purposes:
- Formulation Screening: for selection of lead candidate formulation.
- Bioequivalence: to determine if the new product has the same degree of dermal absorption as reference product.
- Cosmetics and consumer products: in vitro dermal absorption studies are part of safety assessment of a test item.
- Pharmaceutical products: in vitro dermal absorption studies are part of safety and efficacy assessment of topical products.
- Chemical/agrochemical: in vitro dermal absorption studies are part of safety assessment purposes. With respect to pesticides, the results of the in vitro dermal absorption studies alone are accepted for pesticides risk assessment purposes in the European Union and other countries.
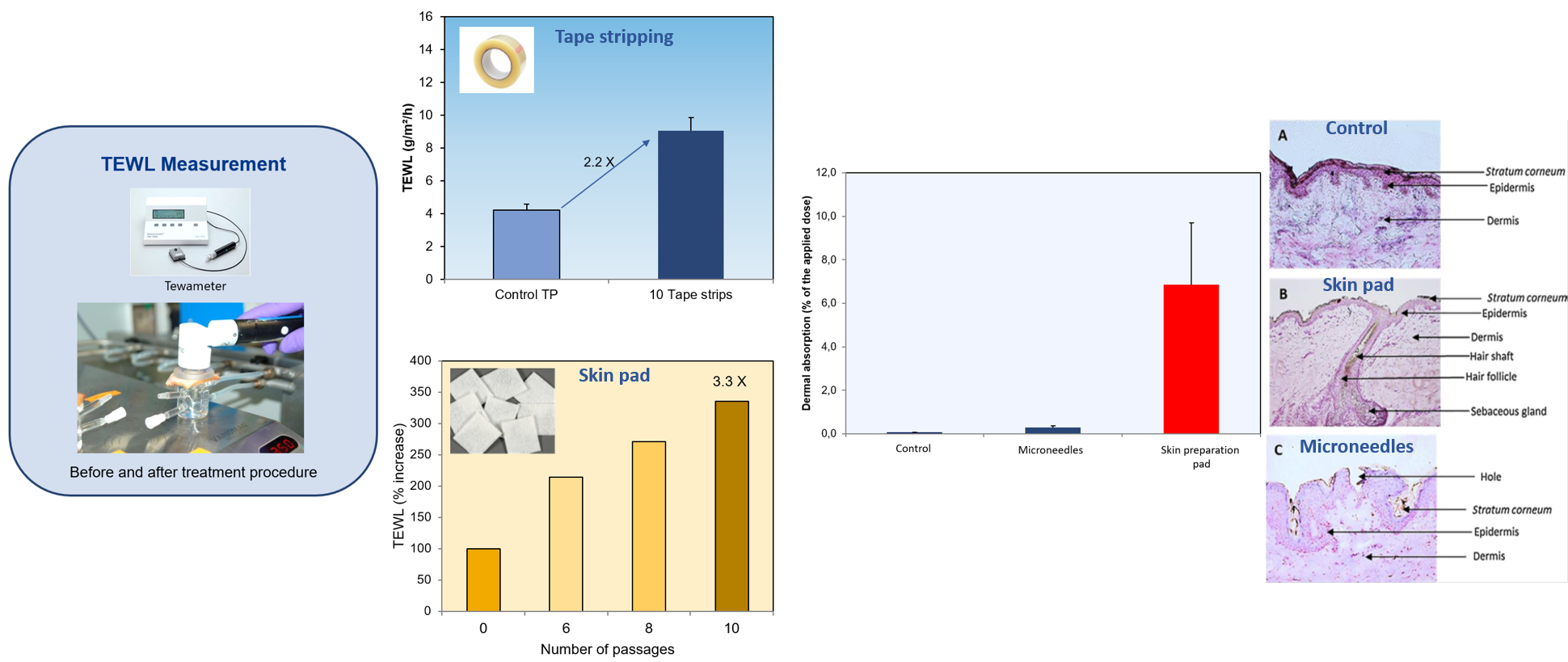
Different types of formulations can be assessed through in vitro dermal absorption studies: creams, gels, ointments, suspensions, foam, patches, aqueous, solvent, hair dyes, shampoo, foundation, moisturizer, cleansers, soaps, sunscreen, and more.
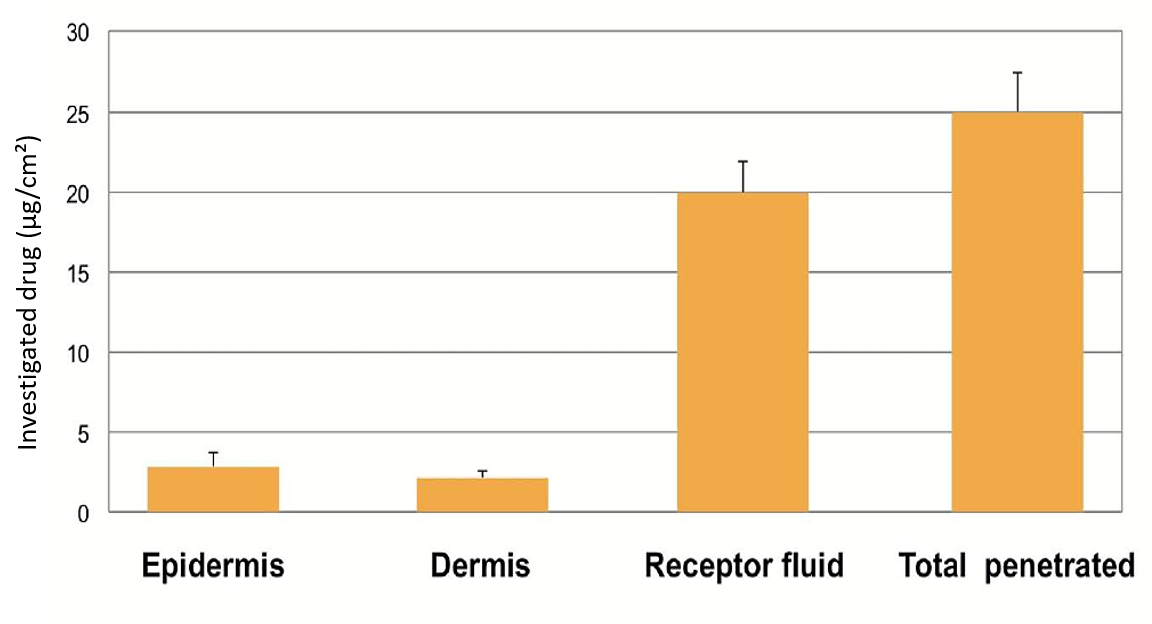
The skin sample is placed between two chambers (a donor chamber and a receptor chamber) of a diffusion cell (Franz diffusion cell) which may be either a static or flow-through set up.

At PKDERM we perform in vitro dermal absorption studies using either Franz-type diffusion cells or our proper model consisting on membrane insert in 6-well plate.
- Frozen skin samples as well as fresh skin samples can be used according to the purpose of the study.
- Treatment duration is set according to use conditions (5 min to 24 h).